Lindol is a revolutionary financial technology platform transforming the way small businesses manage their expenses and budgeting. Offering real-time tracking, insightful analytics, and seamless integration with existing accounting software, Lindol simplifies financial management for entrepreneurs. This infographic highlights key features, benefits, and user experiences that demonstrate Lindol's impact on business efficiency.
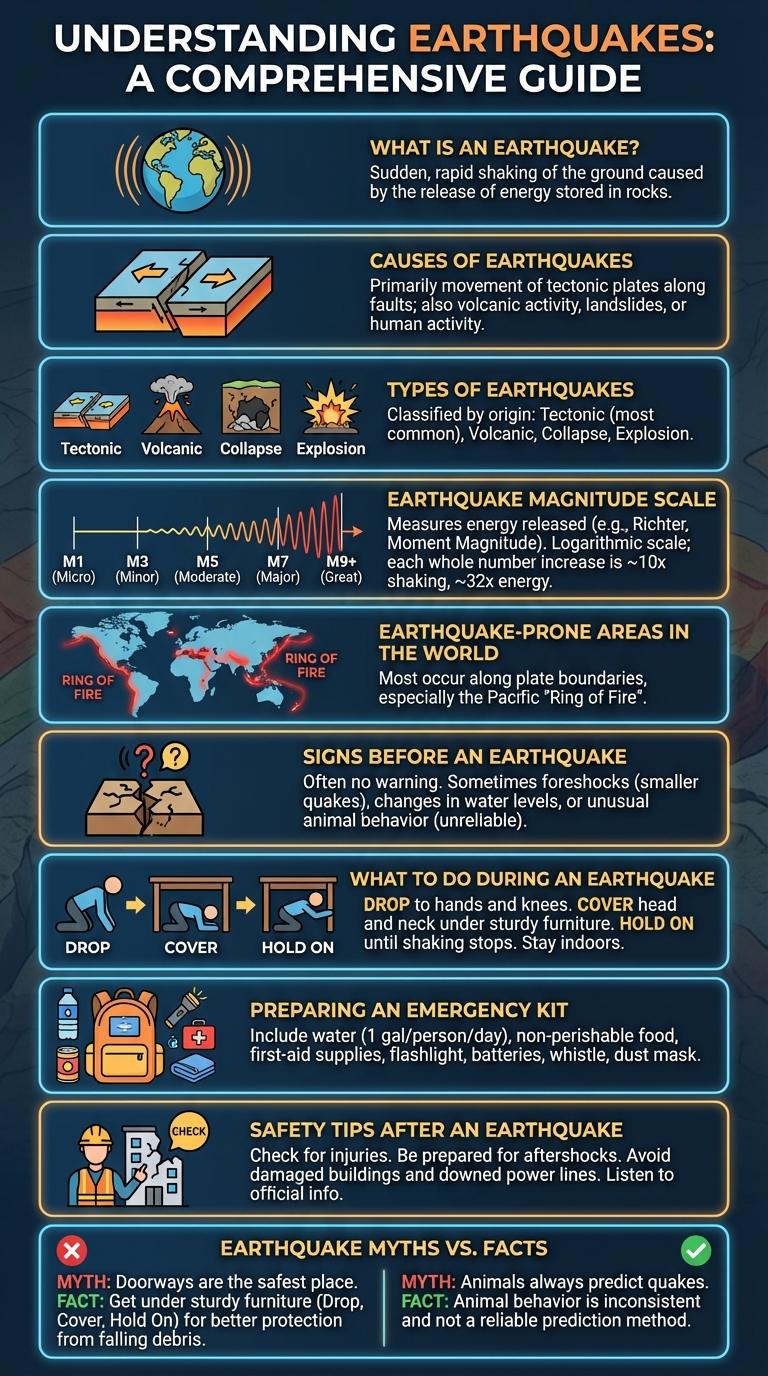
What is an Earthquake?
An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the ground caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface. This movement releases energy that travels in waves, causing the ground to vibrate.
Earthquakes can range from minor tremors to powerful shocks that cause significant damage and loss of life. They commonly occur along fault lines where plates collide, slide past, or pull apart from each other.
Causes of Earthquakes
Earthquakes, known as lindol in Filipino, result from sudden movements in the Earth's crust. These natural events release energy that causes ground shaking.
- Tectonic Plate Movements - The shifting and collision of Earth's plates create stress that triggers earthquakes.
- Volcanic Activity - Magma movement beneath volcanoes can cause seismic disturbances.
- Human Activities - Mining, reservoir-induced seismicity, and underground explosions sometimes induce earthquakes.
Understanding these causes helps in assessing seismic risks and preparing for lindol events.
Types of Earthquakes
Earthquakes, or "lindol" in Filipino, occur due to sudden ground movements caused by tectonic forces. These natural events are classified into different types based on their origin and mechanism.
- Tectonic Earthquakes - Result from the movement of Earth's tectonic plates along faults, causing ground shaking.
- Volcanic Earthquakes - Occur due to volcanic activity, including magma movement beneath the surface.
- Collapse Earthquakes - Triggered by the sudden collapse of underground caves or mines.
Earthquake Magnitude Scale
The earthquake magnitude scale measures the energy released by an earthquake. It helps to determine the earthquake's size and potential impact.
The most commonly used scale is the Richter scale, which assigns a numerical value based on the amplitude of seismic waves. Magnitudes below 3.0 are usually not felt, while those above 7.0 can cause serious damage. Each whole number increase represents roughly 32 times more energy released.
Earthquake-Prone Areas in the World
Earthquakes occur most frequently along tectonic plate boundaries where seismic activity is intense. Certain regions around the world are particularly vulnerable to frequent and strong earthquakes.
- Pacific Ring of Fire - This area encircles the Pacific Ocean and contains about 90% of the world's earthquakes.
- Himalayan Region - The collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates causes frequent seismic activity in this zone.
- Eastern Mediterranean Zone - Earthquakes occur due to the complex interaction between the African, Eurasian, and Arabian plates here.
Signs Before an Earthquake
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Unusual Animal Behavior | Animals such as dogs, cats, and birds may act restless or attempt to escape the area hours or minutes before an earthquake. |
| Ground Vibrations | Minor tremors or vibrations often occur before a stronger quake, sometimes felt as slight shaking or rumbling. |
| Changes in Water Levels | Wells, ponds, or other water bodies may experience sudden fluctuations in water levels due to underground shifts. |
| Unusual Sounds | Low-frequency rumbles or roaring noises sometimes precede earthquakes and can be heard in nearby areas. |
| Cracks in the Ground | New or growing fissures and cracks in soil, roads, or structures may indicate tectonic stress building up. |
What to Do During an Earthquake
During an earthquake, stay calm and drop to the ground to prevent falling. Take cover under sturdy furniture or against an interior wall away from windows. Hold on until the shaking stops to ensure your safety.
Preparing an Emergency Kit
Preparing an emergency kit for a lindol (earthquake) ensures quick access to essential supplies during a crisis. Include water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, a first aid kit, and important documents. Regularly check and update the kit to maintain readiness for any earthquake situation.
Safety Tips After an Earthquake
What should you do immediately after an earthquake?
Check yourself and others for injuries and provide first aid if necessary. Move carefully to avoid hazards like broken glass or unstable structures.
How can you ensure your home is safe to stay in?
Inspect for gas leaks, water leaks, and electrical damage. Shut off utilities if you detect any problems to prevent fires or floods.
Where is the safest place to take shelter post-earthquake?
Stay outdoors away from buildings, trees, streetlights, and utility wires. Find an open area where debris and falling objects are unlikely.
What should you do before re-entering your damaged building?
Wait for official inspections and clearances from emergency responders. Avoid using elevators until they are declared safe to use.
How can you stay informed after an earthquake?
Listen to battery-powered radios or use a mobile device for emergency updates. Follow instructions from local authorities regarding shelter and aid centers.
