Outer space captivates with its vastness, mysteries, and endless discoveries that continue to expand human knowledge. This infographic visualizes key facts about planets, stars, galaxies, and cosmic phenomena, offering an engaging glimpse into the universe's wonders. Explore the data that reveals the scale, composition, and dynamic events shaping the cosmos beyond our planet.
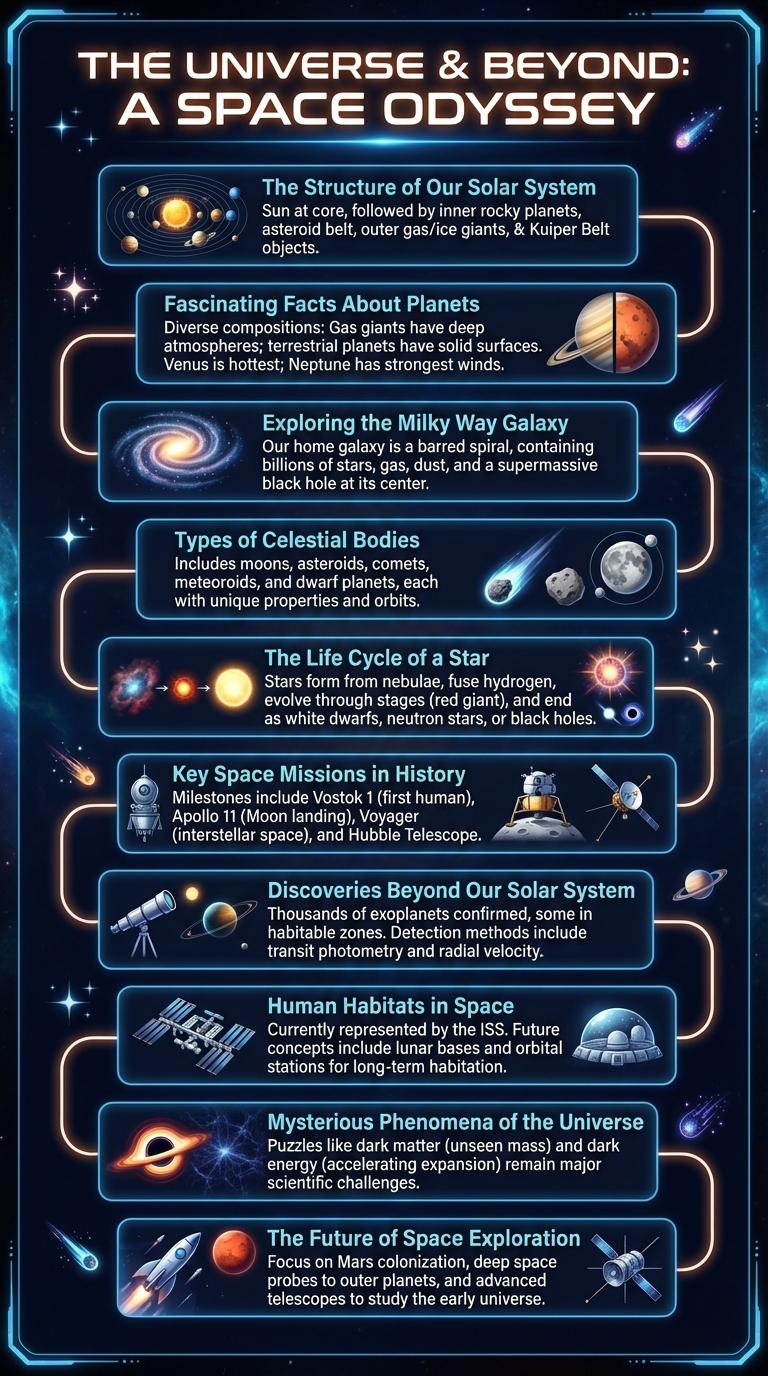
The Structure of Our Solar System
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| The Sun | Central star of the solar system, composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, providing energy through nuclear fusion. |
| Inner Planets | Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars; rocky surfaces and smaller sizes compared to outer planets. |
| Asteroid Belt | Region between Mars and Jupiter containing numerous rocky bodies and minor planets. |
| Outer Planets | Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune; gas giants with thick atmospheres and many moons. |
| Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud | Regions beyond Neptune containing icy bodies, dwarf planets, and comets orbiting the Sun. |
Fascinating Facts About Planets
Outer space holds countless mysteries, with planets offering fascinating insights into our solar system. Each planet has unique characteristics that captivate scientists and space enthusiasts alike.
Jupiter is the largest planet, with a diameter of about 139,820 kilometers, and features a persistent storm known as the Great Red Spot. Mars, called the Red Planet, has the tallest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, standing nearly 22 kilometers high.
Exploring the Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way Galaxy is a vast spiral galaxy, home to our solar system and billions of stars. Exploring it provides crucial insights into the cosmos and our place within it.
Scientists use advanced telescopes and space probes to study the structure and composition of the Milky Way. Key regions of interest include the galactic center, star clusters, and interstellar clouds. Understanding these areas helps reveal the galaxy's formation and evolution over billions of years.
Types of Celestial Bodies
Outer space contains a vast array of celestial bodies, each with unique characteristics and compositions. Understanding these types helps reveal the structure and dynamics of the universe.
- Stars - Massive luminous spheres of plasma that generate energy through nuclear fusion, such as our Sun.
- Planets - Large objects orbiting stars, composed mainly of rock or gas, like Earth and Jupiter.
- Moons - Natural satellites that orbit planets, varying widely in size and geological activity.
- Asteroids - Small rocky bodies primarily found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- Comets - Icy bodies that develop bright comas and tails when approaching the Sun due to sublimation.
The Life Cycle of a Star
The life cycle of a star begins with a nebula, a massive cloud of gas and dust where gravity pulls material together to form a protostar. As the protostar's core temperature rises, nuclear fusion ignites, transforming it into a main sequence star that fuses hydrogen into helium for millions to billions of years. Eventually, the star evolves into a red giant or supergiant before ending its life as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole, depending on its initial mass.
Key Space Missions in History
Outer space exploration has been marked by several key missions that expanded our understanding of the universe. These missions have provided critical data about planets, stars, and cosmic phenomena.
The Apollo 11 mission was the first to successfully land humans on the Moon in 1969. The Voyager probes launched in 1977 continue to send valuable information from beyond our solar system.
Discoveries Beyond Our Solar System
Discoveries beyond our solar system have revolutionized our understanding of the universe. Thousands of exoplanets have been detected using methods such as transit photometry and radial velocity, revealing diverse worlds with varying atmospheres and compositions. Breakthroughs in telescope technology, including the James Webb Space Telescope, continue to unveil distant galaxies, black holes, and cosmic phenomena far beyond our solar neighborhood.
Human Habitats in Space
Human habitats in outer space represent advanced engineering designed to support life beyond Earth. These habitats enable long-term missions in microgravity and hostile environments.
- International Space Station (ISS) - A modular space laboratory that supports scientific research and international collaboration in low Earth orbit.
- Moon Bases - Planned lunar habitats aim to facilitate exploration and resource utilization on the Moon's surface.
- Mars Colonies - Future Mars habitats focus on sustainable living using local materials and closed-loop life support systems.
Developing self-sustaining human habitats is essential for the future of deep space exploration and colonization.
Mysterious Phenomena of the Universe
Outer space is filled with unsolved mysteries that continue to intrigue scientists and astronomers. These phenomena challenge our understanding of the universe and inspire ongoing research.
- Dark Matter - Invisible substance that makes up about 27% of the universe's mass but cannot be directly observed.
- Black Holes - Regions in space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape their pull.
- Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) - Intense, brief flashes of radio waves from distant galaxies with unknown origins.
