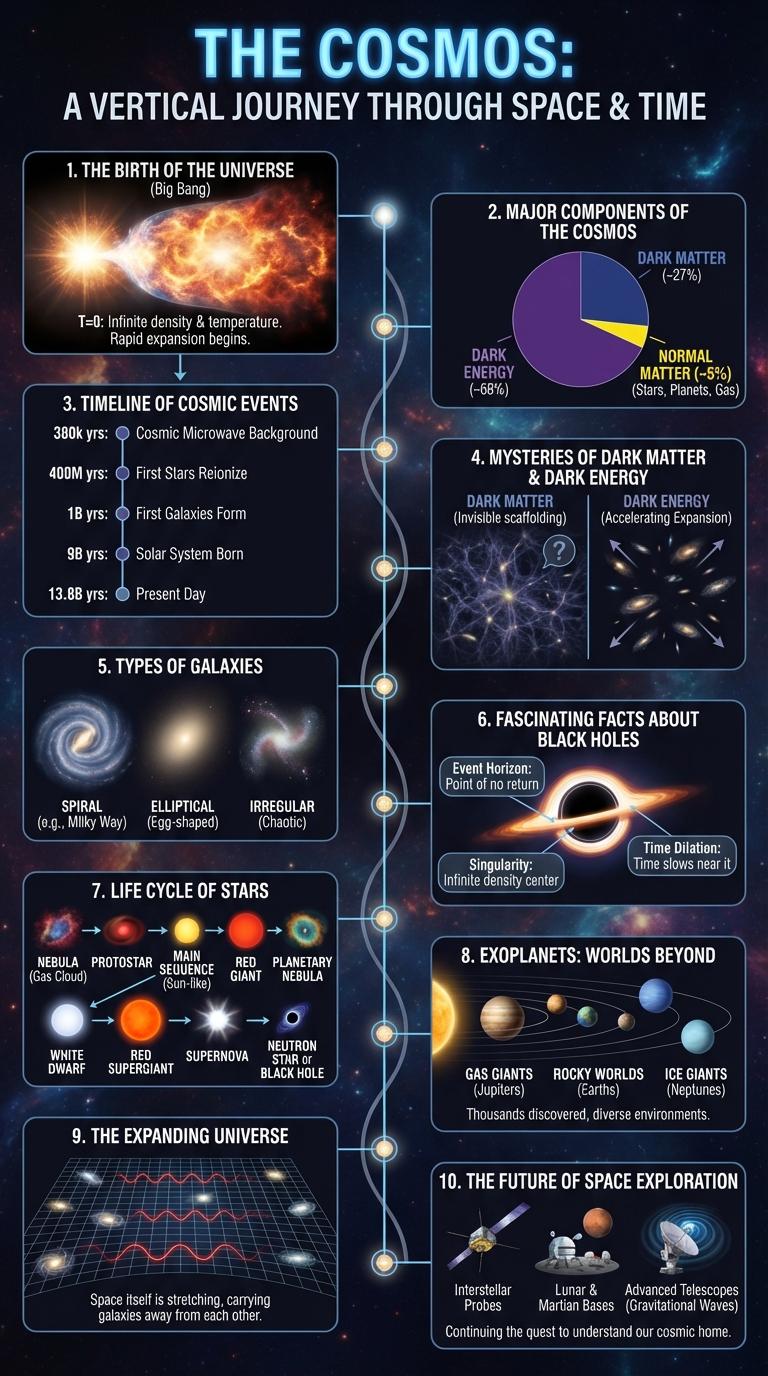
Explore the vast cosmos through a visually engaging infographic that reveals key facts about the universe's scale, composition, and mysteries. This graphic highlights essential astronomical phenomena, from galaxies and black holes to the cosmic microwave background. Discover how space's immense size and complexity shape our understanding of existence beyond Earth.
The Birth of the Universe
The universe began approximately 13.8 billion years ago with the Big Bang, an immense explosion from a singularity. This event marked the origin of space, time, and all matter.
In the first few moments, the universe expanded rapidly in a process called cosmic inflation. Elementary particles formed, eventually leading to the creation of atoms and the first light known as the Cosmic Microwave Background.
Major Components of the Cosmos
The universe is composed of vast and diverse components that shape its structure and behavior. These components include galaxies, stars, planets, dark matter, and dark energy.
Galaxies contain billions of stars, along with gas and dust, forming the main building blocks of the cosmos. Dark matter and dark energy influence the universe's expansion and gravitational effects, making up about 95% of its total mass-energy content.
Timeline of Cosmic Events
| Cosmic Event | Timeframe |
|---|---|
| Big Bang | 13.8 billion years ago |
| Formation of the Milky Way Galaxy | 13.6 billion years ago |
| Formation of the Solar System | 4.6 billion years ago |
| Formation of Earth | 4.5 billion years ago |
| First Life on Earth | Approximately 3.5 billion years ago |
Mysteries of Dark Matter and Dark Energy
The universe is composed of approximately 27% dark matter and 68% dark energy, both of which remain largely mysterious to scientists. Dark matter exerts gravitational effects that influence galaxy formation but does not emit, absorb, or reflect light. Dark energy drives the accelerated expansion of the universe, counteracting gravitational attraction on cosmic scales.
Types of Galaxies
What are the main types of galaxies in the universe? Galaxies are primarily classified into spiral, elliptical, and irregular types based on their shape and structure. Each type contains billions of stars, dust, and dark matter, influencing their formation and evolution.
Fascinating Facts About Black Holes
Black holes are regions in space where gravity is so strong that nothing can escape from them, not even light. These fascinating cosmic objects are formed by the collapse of massive stars and influence their surroundings in profound ways.
- Event Horizon - The boundary around a black hole beyond which nothing can return is called the event horizon.
- Singularity - At the core of a black hole lies the singularity, where density and gravity become infinite.
- Hawking Radiation - Black holes can emit radiation known as Hawking radiation, causing them to slowly lose mass over time.
Life Cycle of Stars
The life cycle of stars showcases the process of stellar birth, evolution, and eventual demise within the universe. Understanding these stages reveals the mechanisms behind star formation and cosmic transformations.
- Stellar Nebula - Stars begin their life as dense clouds of gas and dust called stellar nebulas.
- Main Sequence Star - The star enters the main sequence phase, where nuclear fusion converts hydrogen into helium, producing energy.
- Red Giant or Supergiant - As hydrogen depletes, the star expands and cools, forming a red giant or supergiant depending on its mass.
- Stellar Death - Low-mass stars become white dwarfs, while high-mass stars explode as supernovae, leading to neutron stars or black holes.
- Stellar Remnants - The remaining stellar core becomes a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole, completing the star's life cycle.
Exoplanets: Worlds Beyond Our Solar System
Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars outside our solar system, revealing the vast diversity of worlds in the universe. These distant planets provide critical clues about planetary formation and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Since the first confirmed discovery in 1992, thousands of exoplanets have been identified using methods like the transit and radial velocity techniques. They range from gas giants larger than Jupiter to rocky Earth-like planets in the habitable zone. Studying exoplanets helps astronomers understand the conditions necessary for life and the evolution of planetary systems.
The Expanding Universe
The universe is continuously expanding, a phenomenon first observed by Edwin Hubble. This expansion influences the distance between galaxies and the overall structure of the cosmos.
- Hubble's Law - The recessional velocity of galaxies increases with their distance from Earth.
- Cosmic Microwave Background - Radiation providing evidence for the Big Bang and ongoing expansion.
- Dark Energy - A mysterious force accelerating the expansion of the universe.
The expanding universe shapes cosmic evolution and affects the fate of all celestial bodies within it.
