Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than infrared light, widely used in communication technologies. They enable wireless transmission of signals for radios, televisions, and mobile devices, making them essential for modern connectivity. Understanding the properties and applications of radio waves helps in optimizing communication systems and advancing technology.
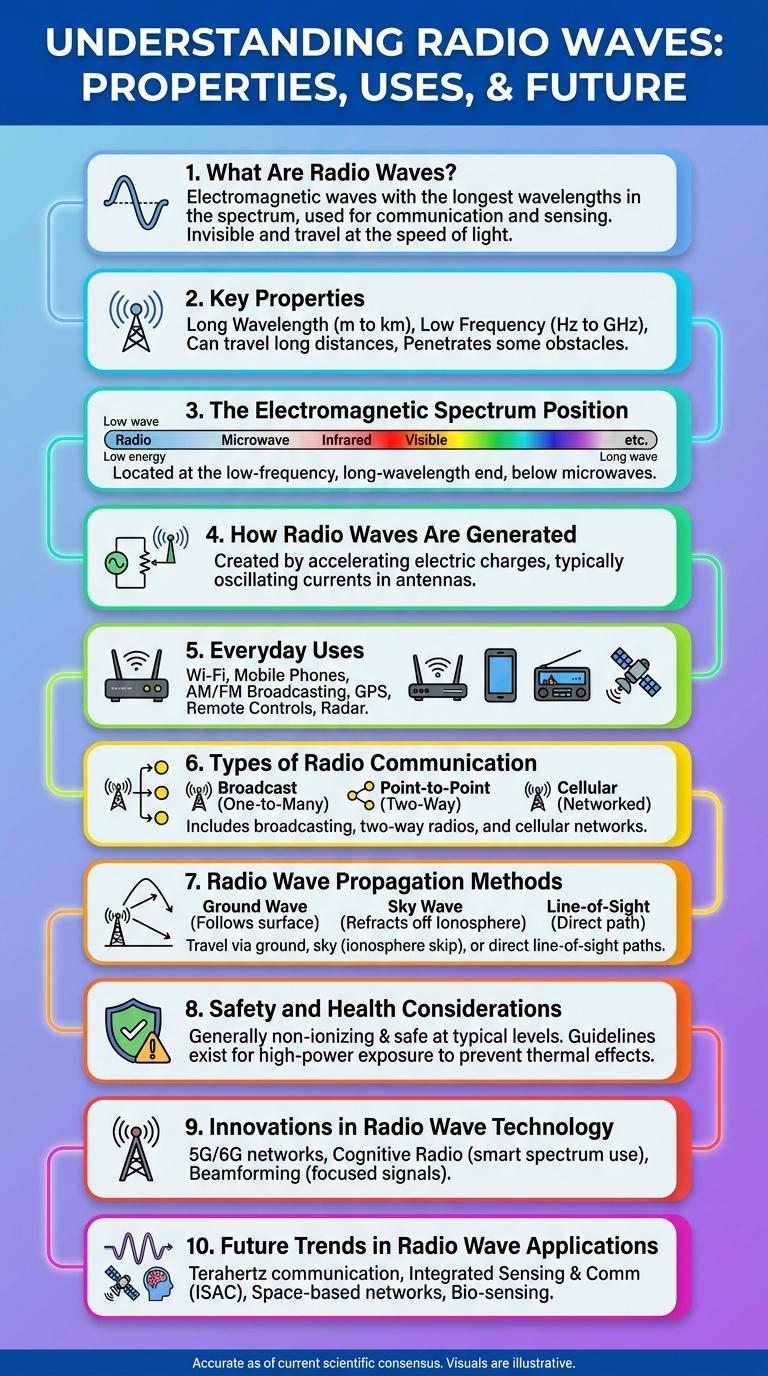
What Are Radio Waves?
What Are Radio Waves?
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than infrared light. They are used for wireless communication, including radio, television, and mobile phones.
Key Properties of Radio Waves
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 3 kHz to 300 GHz, covering longwave to millimeter waves |
| Wavelength | Varies from 100 km (longwave) to 1 mm (millimeter waves) |
| Propagation | Capable of ground wave, skywave, and line-of-sight transmission |
| Speed | Travels at the speed of light, approximately 299,792 km/s in a vacuum |
| Penetration | Ability to pass through certain materials like buildings and atmosphere with varying attenuation |
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Position
Radio waves occupy the lowest frequency range in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically from 3 kHz to 300 GHz. These waves have the longest wavelengths, ranging from a few millimeters to several kilometers.
Positioned below microwaves, radio waves are essential for communication technologies like broadcasting, radar, and satellite transmissions. Their low frequency allows them to travel long distances and penetrate various materials. This unique placement makes radio waves vital for wireless information transfer across the globe.
How Radio Waves Are Generated
Radio waves are generated by the movement of electrons in an antenna. When electric current oscillates, it creates electromagnetic waves that propagate through space.
- Oscillating Current - Alternating current in the antenna produces changing electric and magnetic fields.
- Electron Acceleration - Accelerated electrons emit energy as radio frequency waves.
- Transmission Antenna - The antenna radiates the generated radio waves into the surrounding environment.
Everyday Uses of Radio Waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation used in everyday communication technologies such as television, radio broadcasting, and mobile phones. They enable wireless transmission of data, allowing devices to connect without physical cables. These waves also play a crucial role in GPS navigation and emergency communication systems.
Types of Radio Communication
Radio waves enable various types of radio communication, each serving distinct purposes and ranges. Common types include AM and FM broadcasting, used for audio transmission over long distances. Other important types are mobile communication, satellite communication, and radar systems, which support connectivity, navigation, and detection.
Radio Wave Propagation Methods
Radio wave propagation refers to the ways radio signals travel from a transmitter to a receiver. Understanding propagation methods is essential for effective communication system design.
There are three primary types of radio wave propagation: ground wave, sky wave, and line-of-sight. Each method varies based on frequency, distance, and environmental factors.
Safety and Health Considerations
Radio waves are a form of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation used in communication technologies. Understanding their safety and health considerations is crucial for minimizing potential risks.
- Non-Ionizing Radiation - Radio waves do not carry enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules in the human body.
- Exposure Limits - International guidelines set limits on radio wave exposure to prevent thermal and non-thermal effects.
- Thermal Effects - High levels of radio wave exposure can cause tissue heating, but typical exposure levels are far below this threshold.
Regulatory agencies continuously monitor research to ensure radio wave exposure remains safe for public health.
Innovations in Radio Wave Technology
Radio wave technology has undergone significant advancements that enhance communication and data transmission. Innovations focus on increasing efficiency, range, and signal clarity to meet modern demands.
- 5G Network Deployment - Utilizes high-frequency radio waves to provide faster internet speeds and lower latency for mobile devices.
- Software-Defined Radio (SDR) - Enables flexible radio communication systems through software rather than hardware modifications.
- Massive MIMO Technology - Employs multiple antennas to improve capacity and signal strength in wireless networks.
