Research infographics visually represent complex data, making information easier to understand and share. They combine graphics, statistics, and concise text to highlight key findings and trends in a clear, engaging format. This approach enhances comprehension and retention of research insights for diverse audiences.
The Research Process Explained
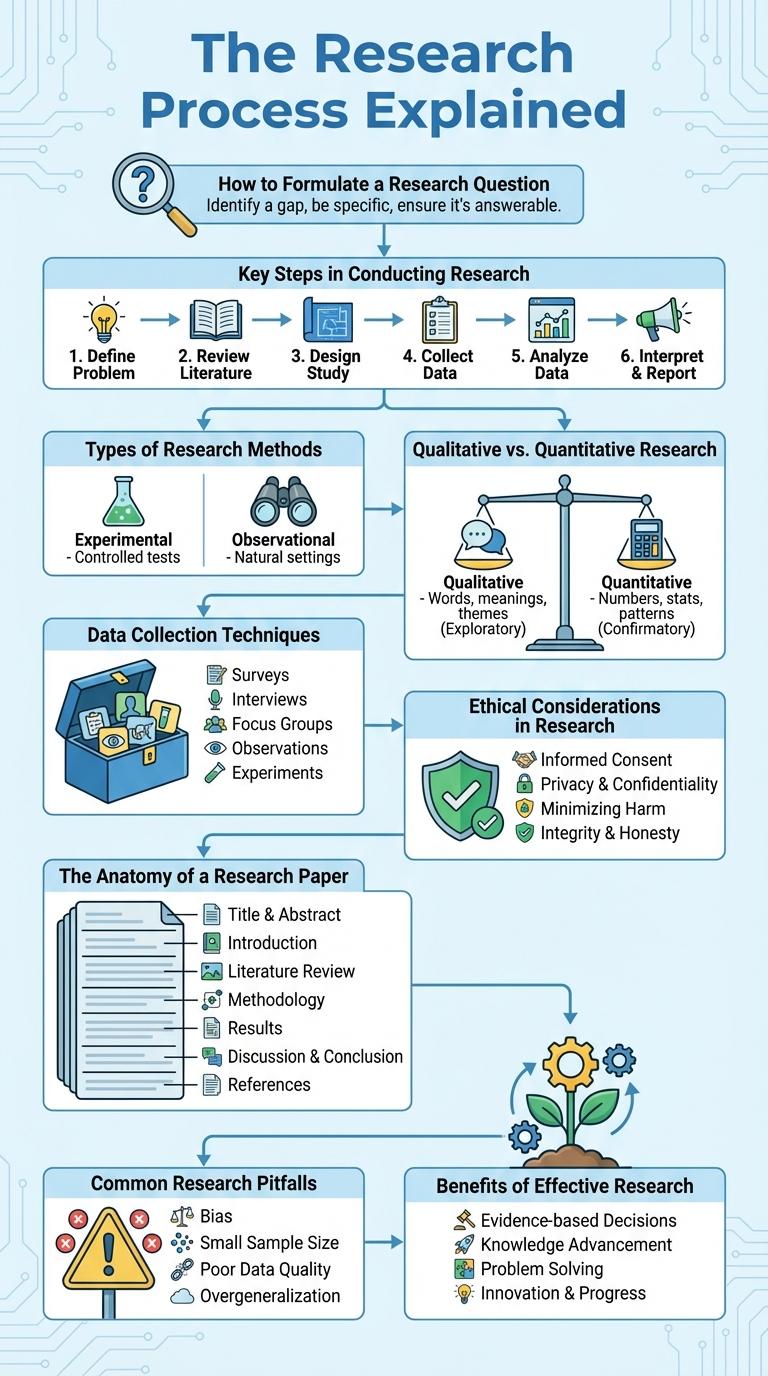
The research process is a systematic series of steps guiding the investigation from question formulation to conclusion. It ensures reliable results by following structured methods and critical analysis.
This process includes defining the problem, reviewing existing knowledge, designing the study, collecting data, analyzing findings, and drawing conclusions. Each phase is crucial for producing valid, credible research outcomes.
Key Steps in Conducting Research
Research involves a systematic process to gather and analyze information. Key steps include defining the research question, collecting relevant data, and analyzing the findings to draw conclusions. Proper planning and execution ensure the accuracy and reliability of the research outcomes.
Types of Research Methods
| Type of Research Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Qualitative Research | Explores phenomena through non-numerical data like interviews, observations, and text analysis to understand meanings and experiences. |
| Quantitative Research | Collects and analyzes numerical data using statistical methods to test hypotheses and identify relationships. |
| Mixed Methods | Combines qualitative and quantitative approaches to provide comprehensive insights by integrating numerical data with contextual understanding. |
| Experimental Research | Investigates cause-and-effect relationships by manipulating variables in controlled environments to measure outcomes. |
| Descriptive Research | Gathers detailed information to describe characteristics or functions of a subject without influencing variables. |
The Anatomy of a Research Paper
An infographic about the anatomy of a research paper highlights its core components: Title, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References. Each section serves a distinct purpose, guiding readers through the study's objectives, methodology, findings, and implications. Understanding this structure enhances reading comprehension and facilitates effective scientific communication.
Data Collection Techniques
Data collection techniques are essential methods used in research to gather accurate and relevant information for analysis. These techniques vary based on the research design, objectives, and type of data required.
Common data collection methods include surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments. Choosing the appropriate technique ensures data validity, reliability, and efficiency in achieving research goals.
Common Research Pitfalls
Research is a critical process that requires careful planning and execution to yield valid results. Awareness of common pitfalls can improve the quality and reliability of research outcomes.
- Poorly Defined Research Question - Ambiguous or overly broad questions can lead to unclear objectives and inefficient study design.
- Inadequate Sample Size - Small or non-representative samples reduce the generalizability of findings and increase error margins.
- Data Collection Bias - Systematic errors during data gathering can distort results and impact the study's validity.
Benefits of Effective Research
Effective research drives innovation and informed decision-making in various fields. It uncovers essential insights that contribute to scientific, economic, and social advancements.
Research enhances knowledge accuracy, reducing errors and misconceptions. It supports evidence-based practices, improving outcomes in healthcare, education, and technology. Organizations benefit from competitive advantages by leveraging research findings for strategic growth.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Research methods can be broadly divided into qualitative and quantitative approaches, each serving different purposes and data types. Understanding their distinctions is essential for effective study design and data analysis.
- Qualitative Research - Focuses on exploring concepts, experiences, and understanding meanings through open-ended data collection methods like interviews and observations.
- Quantitative Research - Involves numerical data collection and statistical analysis to quantify variables and identify patterns or correlations.
- Data Nature - Qualitative data is descriptive and subjective, while quantitative data is structured and objective.
- Sample Size - Qualitative studies often use smaller, purposive samples, whereas quantitative research relies on larger, representative samples.
- Outcome Purpose - Qualitative research aims to generate theories and insights; quantitative research tests hypotheses and measures effects.
How to Formulate a Research Question
Formulating a clear research question is a critical first step in any research process. A well-defined question guides the entire study and ensures focused, meaningful outcomes.
- Identify a topic - Choose a broad subject area related to your interests or field of study.
- Conduct preliminary research - Review existing literature to understand current knowledge and gaps.
- Narrow your focus - Refine the topic into a specific, manageable question that addresses a precise issue.
A strong research question is clear, focused, and researchable, setting the foundation for successful investigation.
